Investment options offering fixed returns are quite popular among investors who wish to growth their money without taking risks associated with market fluctuations. Fixed Deposits (FDs) and Recurring Deposits (RDs) are the two such products. These are popular investment options offered by banks and financial institutions, with their own set of features and benefits. However, before making any investment, understanding the difference between the two can help in taking an informed decision based on one’s financial goals and preferences.
FDs are secure investment options. When you invest in an FD, you deposit a lump sum amount with a bank or financial institution for a predetermined period at a fixed interest rate. This interest rate remains constant throughout the tenure of the deposit, offering stability and predictability in returns. FDs usually have varying tenure options, ranging from a few days to several years. The interest earned on FDs is higher compared to savings accounts, making it an attractive option for individuals looking for stable returns.
Read More: SBI FD Scheme: Rs 10 lakh will become Rs 20 lakh without any market risk; know how
On the other hand, Recurring Deposits (RDs) are a systematic way of saving money on a regular basis. In an RD, investors deposit a fixed amount at regular intervals, typically monthly, with the bank or financial institution. These deposits accumulate over time and earn interest similar to FDs. RDs also come with predefined tenure, and the interest rates offered are usually similar to those of FDs.
Adhil Shetty, CEO, Bankbazaar.com, says, “One of the primary differences between FDs and RDs lies in the mode of investment. FDs require a lump sum amount to be deposited initially, while RDs allow investors to contribute smaller amounts at regular intervals.”
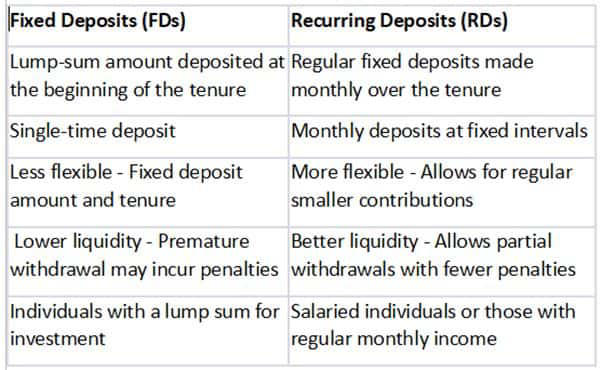
In terms of liquidity too, FDs and RDs differ. FDs are less liquid compared to RDs, as breaking an FD prematurely might attract penalties or result in lower interest earnings. RDs, on the other hand, offer more flexibility, allowing investors to withdraw the accumulated amount with lesser penalties compared to premature withdrawal from FDs.
When it comes to the return, the interest rates offered on FDs and RDs depend on various factors such as the deposit amount, tenure, and prevailing market conditions. Generally, FDs tend to offer slightly higher interest rates compared to RDs, especially for longer tenures or larger deposit amounts.
Read More: Rupee Up 2 Paise To 83.25 Against US Dollar In Early Trade
Tax implications also play a role in deciding between FDs and RDs. The interest earned on both FDs and RDs is taxable as per the investor’s income tax slab. However, TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) is applicable if the interest earned exceeds a certain threshold. Additionally, senior citizens often enjoy higher interest rates and tax benefits on FD investments.
Choosing between FDs and RDs depends on individual financial goals and liquidity requirements. If you have a lump sum amount and seek higher returns with fixed interest rates, FDs might be more suitable. Conversely, if you prefer disciplined savings with smaller regular contributions and flexibility in withdrawals, RDs could be the better option.
It is advisable to have diversifying investments across different instruments that can help in mitigating risks and optimising returns while ensuring a mix of liquidity and stability in the investment portfolio.





































