GURUGRAM: As the Haryana government gears up to observe World Water Day on Monday, not much has been done to improve the city’s groundwater level, which has been declining at an alarming rate for several years now.
Gurugram witnessed a fall of 5 metres in its water table over the last two years, according to post-monsoon data recorded by the agricultural department’s groundwater cell. The city’s average groundwater level is around 38.7m at present. In the last 10 years, the water levels of the entire district have dipped by 7.7m.
The city has already been marked as a ‘dark zone’ by Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA).
The city’s water extraction is three times more than its recharge, according to groundwater experts. Illegal groundwater extraction, however, is being carried out blatantly, with little action taken by the authorities.
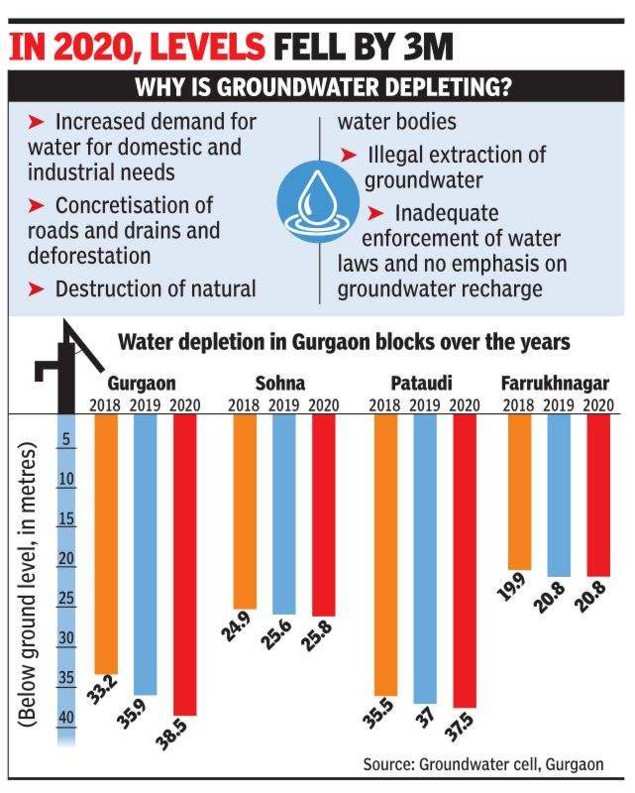
The groundwater cell’s records show that water depletion is the highest in Gurugram block. In 2018, the average groundwater level in Gurugram was 33.2m, which dipped to 35.9m in 2019 and 38.5m last year.
Meanwhile, Sohna block’s groundwater level stood at 24.9m in 2018, 25.6m in 2019 and 25.8m in 2020. In Pataudi block, it was 35.5m in 2018, 37m in 2019 and 37.5m in 2020. Farrukhnagar has reported far less fluctuations — while the water table stood at 19.9m in 2018, it dipped to 20.8m in 2019. Its water table hovered around the same mark last year.
“We have collected samples from 62 pits across the district, which are used to record average groundwater levels twice a year. Pre-monsoon levels are recorded in June and post-monsoon levels in October, after which we analyse the groundwater of different blocks. It has been observed that there is a steady decline in Gurugram’s groundwater table, up to 2.5m on an average every year,” said VS Lamba, Gurugram’s chief hydrologist.
He said depletion is more in urban areas compared to rural areas and pointed out the major cause for these heavy losses: a vicious cycle of real estate development and population growth. Commercial highrises and residential apartments generally have their own water extraction units like borewells inside their premises to draw large amounts of water, according to water experts.
In Chakkarpur, Baliawas, Sikanderpur and Udyog Vihar, the water table has dropped to over 75m below ground level. Other areas reporting high depletion include Gurugram village, Civil Lines, Wazirabad and Kasan, where the water table has dropped to over 48m. Similarly, it has dipped to around 50m in parts of DLF City, Sohna Road and Sector 56 due to a high concentration of residential complexes.
Experts say the development boom in the city took local authorities by surprise and they did not plan adequately for the power and water needs of the burgeoning population.





































